PICALM kiinnittyy PIP2:n kalvossa kohdallaan jossa on lysiinejä K kolme ja yksi histidiini H. Lysiini on essentielli aminohappo ja histidiini on joissain tapauksissa essentielli aminohappo.
PIP2 rakenne on modulimainen ja kaikissa PIP2 muodoissa on inositolirengas, ja siinä fosfaatteja sekä fosfatidyyli, jossa on kaksi rasvahappoa. Tämä fosfatidyylikohta on kuin se varsi, jolla moduli on petautunut palsamkalvolipidien joukkoon.
Näillä rasvahapoilla on myös geneettinen preferenssinsä. Glyserolirakenne joka on pohjilla näissä moduleissa, ottaa sn1 asemaan mieluyiten steariinihappoa, jota keho tuottaa etikkahaposta käsin palmitiinihapon kautta. Sn2 asemaan valikoituu mieluiten essentielli aminohapposyntyinen arakidonihapp . Sitä keho tekee ravinnon linolihapost käsin. ja sitä onkin siten kehon joka solussa normaalisti.
Mikä preferenssi on PIP2 modulin kokoontumsiessa neurologisessa kudoksessa, onko se tämä sama yleinen? Tietysti näitä tutkimuksia on tehtykin paljon ja niitä vain tulee löytää. Itselläkin pitäisi josain vihossa olla luettelo tästä eri fosfolipidien tavasta valikoida rakenteensa rasvahapot.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylinositol
The specific fatty acids of PtdIns, and their conformation, employed in the sensory neurons has not been elucidated. (Aug 2018).
----
Steariinihapon synteesi tapahtuu etikkahaposta (C2:0) käsin C18:0 kokoon.
(Steariinihaposta 4 artikkelia):
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28757255
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21732666
BMC Neurosci. 2004 Apr 20;5:15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15099403 Regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 after central and peripheral nerve lesions.Breuer S1, Pech K, Buss A, Spitzer C, Ozols J, Hol EM, Heussen N, Noth J, Schwaiger FW, Schmitt AB. Department of Neurology, University Medical School, Pauwelsstr 30, D-52074 Aachen, Germany.
Abstract BACKGROUND:
Interruption
of mature axons activates a cascade of events in neuronal cell bodies
which leads to various outcomes from functional regeneration in the PNS
to the failure of any significant regeneration in the CNS.
One factor which seems to play an important role in the molecular
programs after axotomy is the stearoyl Coenzyme A-desaturase-1 (SCD-1).
This enzyme is needed for the conversion of stearate (C18:0)
into oleate (C18:1). Beside its role in membrane synthesis, oleate could act as
a neurotrophic factor, involved in signal transduction pathways via
activation of protein kinases C. RESULTS: In situ
hybridization and immunohistochemistry demonstrated a strong
up-regulation of SCD at mRNA and protein level in regenerating neurons
of the rat facial nucleus whereas non-regenerating Clarke's and Red
nucleus neurons did not show an induction of this gene. CONCLUSION: This differential expression points to a functionally significant role for the SCD-1 in the process of regeneration. PMID: 15099403 PMCID: PMC411035 DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-5-15 [Indexed for MEDLINE]
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7463084
Myeliinin gangliosidit kananpojilla ja kyyhkysillä on tutkittu ja rasvahappokoostumuksia verrattu imettäväisten gangliosideihin. Steariinihappo oli yleinen rasvahapporyhmässä, 10 prosenttia C20.-sfingosiinista.
Fatty acids of this ganglioside included both the hydroxy- and
unsubstituted types, and long-chain bases were almost entirely C18.
Ganglioside GM1 split into two closely migrating bands on TLC, the
slower of which resembled mammalian GM1 in having stearate as the main fatty acid with a measurable amount (10%) of C20-sphingosine;
- Entä jos puuttuu SCD1 aktiivisuus, eikä stearaatti voi muuttua öljyhapoksi hermokudoksessa?
- Leptiinin ( fysiologisesti ilmeisesti ) tulisi aktivoida SCD1 suorittamaan konversio.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28768997/
Leptiini ja neurodegeneraatio?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=leptin%2C+neurodegeneration
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0028390817306226?via%3Dihub
Tässä artikkeli joka kannattaa suomentaakin.
https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/413613/fncel-12-00340-HTML/image_m/fncel-12-00340-g002.jpg
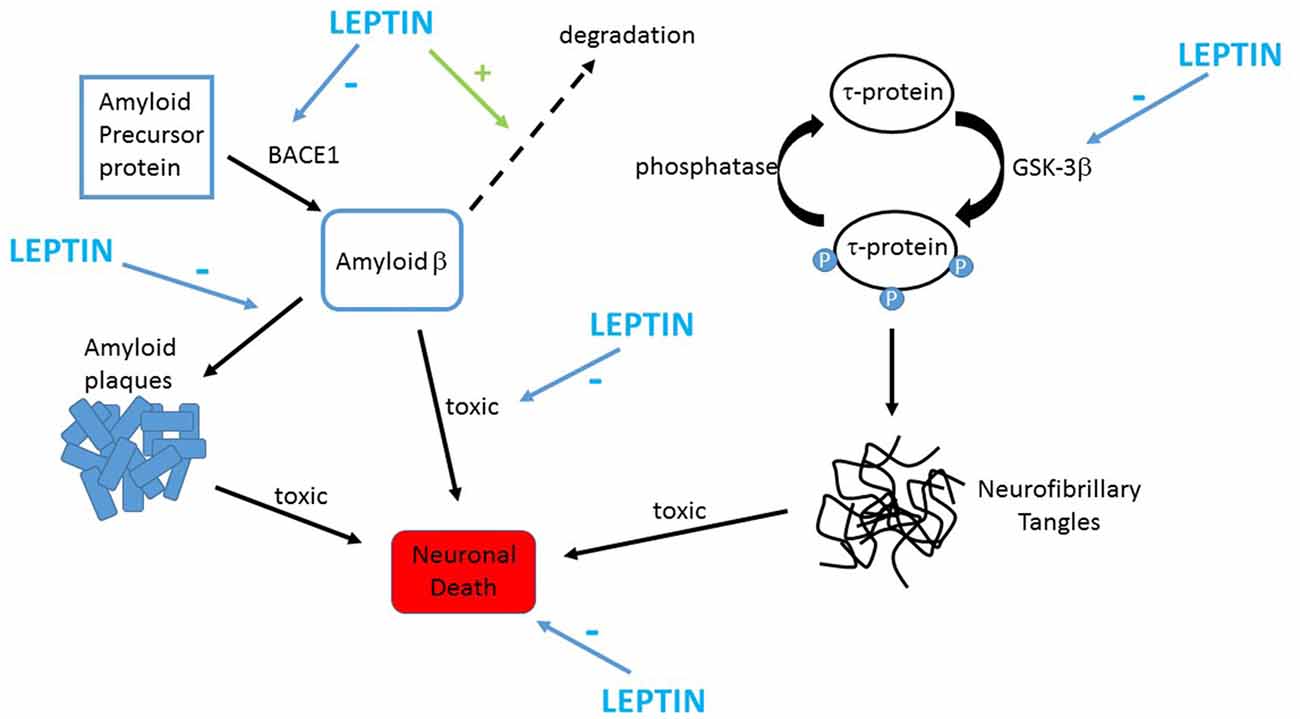
...steariinihappopointsu.. Jatkuu.. 3.10.2019
Huom. ajattele steariinikynttilöitä. Steariinihappo on kovaa rasvaa. Leptiini- jos se toimii, stimuloi sen muuttumista ( desaturoitumista) MUFA hapoksi, joka on öljyhappo.
LEPTIINI vaikuttaa olevan aika olennaisessa kohdasas toimiva peptidi "Obesity factor"- jos sen toiminta vikuuntuu, aiheutuu ylipainoa ja painonvakauden menetys, diabeettisuutat (DM2) ym.
Se vaikuttaa myös että Abeeta degradoituu, joten sen vikatoiminta on tekijä myös Ad-taudissa.
Otan sivuhypyn:
Leptiinireseptori ja leptiini.



