Tämä oli ensimmäinen laajempi fytiinitaulukko, minkä löysin vuonna 2005.
LÄHDE: Spiller Gene A. Phytate Contents of Foods In: Dietary Fiber in human Nutrition
Jos poimin esiin kymmenen kaikkein fytiinipitoisinta elintarviketta -pari päälle - saan seuraavan asiaa valaisevan listan:
1. VEHNÄN IDUT, 4600 mg/ 100 g
2. VEHNÄN LESEET,3360 mg/ 100 g
3. KUIVAT SOIJAPAVUT, 2580 mg/ 100g
4. UNIKONSIEMENET, 2316 mg/ 100g
5. VILLIRIISI, 2200 mg/ 100 g
6. MAISSIROUHEPUURO, 2186 mg/ 100 g
7. TUMMAT SAKSANPÄHKINÄT,2040 mg/ 100 g
8. KURPITSAN SIEMENET,1998 mg/ 100 g
9. CASHEWPÄHKINÄT,1968 mg/ 100g
10. KAAKAOJAUHO, 1960 mg/ 100g
11. TOMAATIN SIEMENET,1955 mg/ 100 g
12. SEESAMIN SIEMENET,1710 mg/ 100 g
13 AURINGONKUKAN SIEMENET,1699 mg/ 100 g
Löytyy toinen lähde myös 23.7. 2014 Pitää ottaa sitaatti, ettei linkki katoa kun jokin aika on kulunut.
http://www.precisionnutrition.com/all-about-phytates-phytic-acid
"ALL ABOUT" SERIES
All About Phytates (Phytic Acid)
Phytic acid – the storage form of phosphorus – is one of those
pesky “anti-nutrients” the Paleo community keeps telling you to avoid.
It’s often considered an anti-nutrient because it binds minerals in the digestive tract, making them less available to our bodies.
Yet these same anti-nutrient properties can also help in the prevention of chronic disease.
The tables below compare various seed types according to their phytic acid/phytate content.
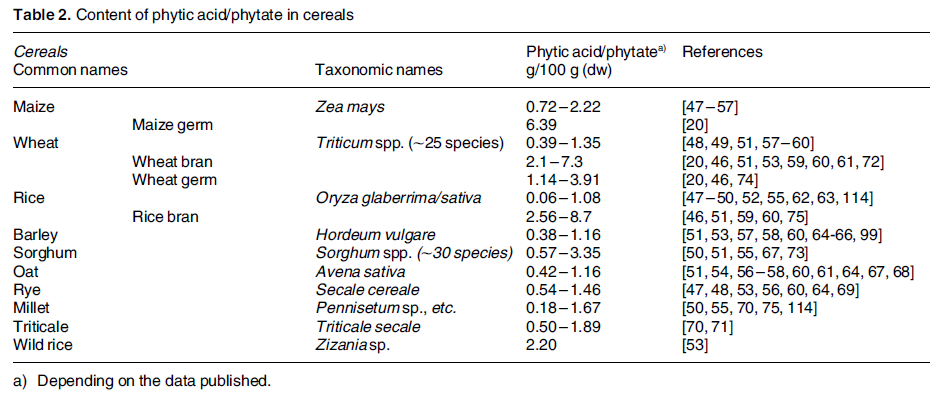
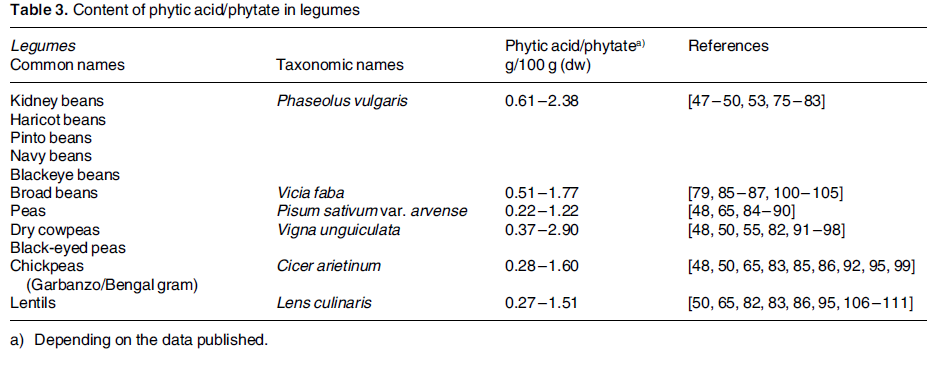
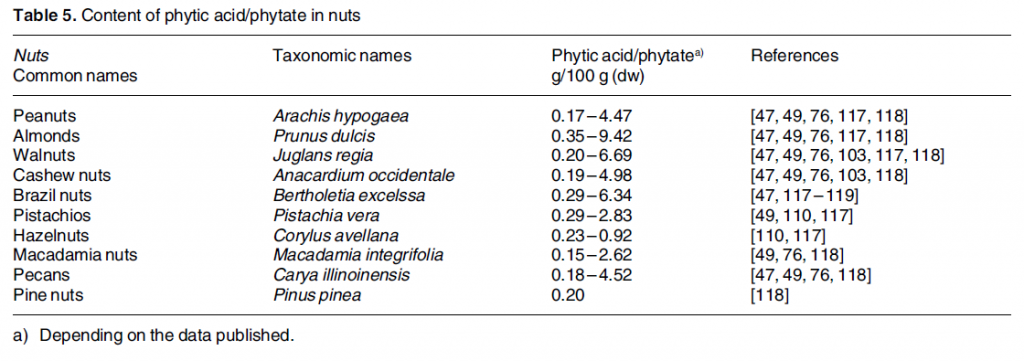
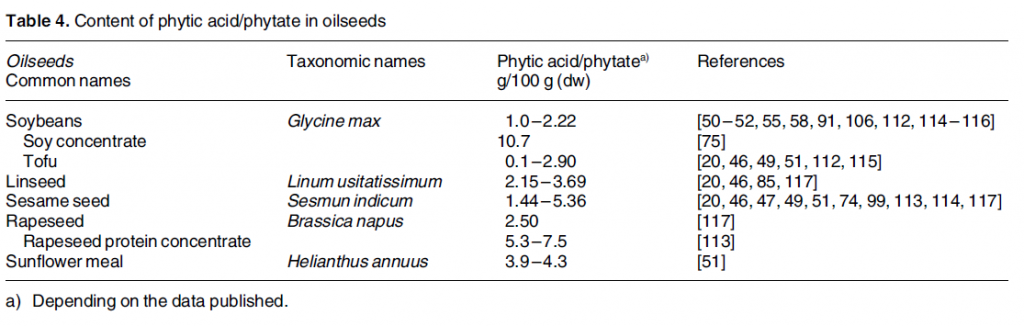 As you can see, phytic acid content varies greatly among plants.
This is due to the type of seed, environmental condition, climate, soil
quality, how phytate is measured in the lab, and so forth.
As you can see, phytic acid content varies greatly among plants.
This is due to the type of seed, environmental condition, climate, soil
quality, how phytate is measured in the lab, and so forth.
Roots, tubers, and other vegetables may also contain phytic acid, but usually in lower amounts.
The most concentrated sources tend to be whole grains and beans. Phytic acid is isolated in the aleurone layer in most grains, making it more concentrated in the bran. In legumes, it’s found in the cotyledon layer (where the protein is).
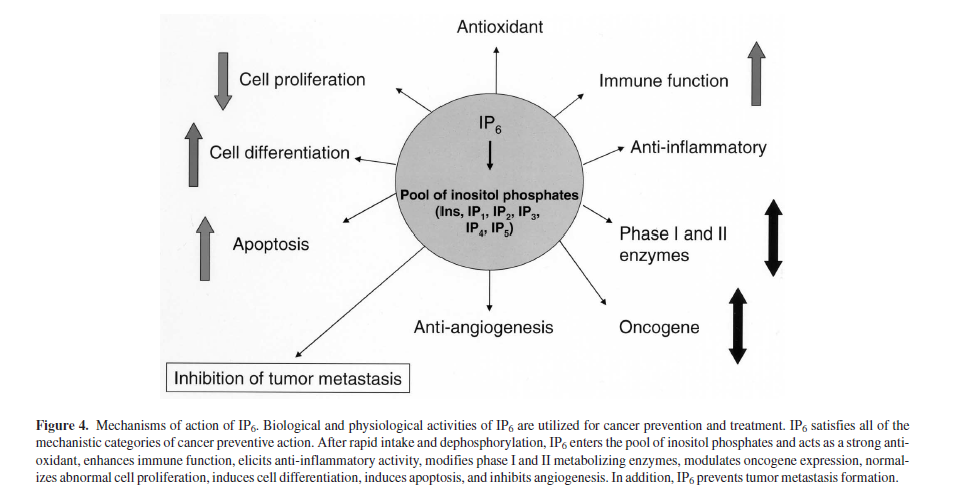
Phytates perform an essential role in plants, as they are an energy source for the sprouting seed. When a seed sprouts, phytase enzymes break down the stored phytates. When we eat the plant, phytates are hydrolyzed during digestion to myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexkisphosphate (IP6) and lower inositol polyphosphates including IP1 through IP5 (these are phytate degradation products).
As you can imagine, intake tends to be much higher among those who follow non-Westernized diets. In developing countries, plants are staple foods, which means people eat more of them, and therefore get more phytic acid.
In developed countries, plant-based or vegetarian eaters tend to consume more phytic acid than omnivores. Further, males usually consume more phytic acid than females, simply because they eat more food.
Ordinarily, our bodies regulate phytate levels pretty well, adjusting uptake in the gut and excretion until body levels come into balance.
Vitamin D status in the body seems to influence how much phytate is actually retained. The more vitamin D, the more phytate retained; the less vitamin D, the less phytate retained.
Here’s an example.
Vegan eaters often consume more iron than omnivores. Yet, they also consume more anti-nutrients, including phytates, and these reduce the amount of iron available to their bodies. Consuming 5-10 mg of phytic acid can reduce iron absorption by 50%.
This is why vegetarian eaters should eat more iron than omnivores (33 mg for veg eaters vs. 18 mg for omnivores).
While in the intestines, phytic acid can bind the minerals iron,
zinc, and manganese. Once bound, they are then excreted in waste.
This can be a good or bad thing, depending on the condition. It’s a bad thing if you’re having trouble building up iron stores in the body and have developed iron-deficiency anemia.
When is it a good thing? Keep reading – you’ll find potential benefits of phytic acid below.
Some experts even suggest that it’s the phytic acid in whole grains and beans that lends them their apparent protective properties against cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
(Remember, the grains with little to no phytic acid are the refined ones.)
The supplement industry has caught on to this. Have you even seen a bottle of inositol hexaphosphate, or IP6? That’s simply a supplemental source of phytic acid.
When phytic acid binds minerals in the gut, it prevents the formation of free radicals, thus making it an antioxidant. Not only that, but it seems to bind heavy metals (e.g., cadmium, lead) helping to prevent their accumulation in the body
Those who consume more phytic acid are less likely to succumb to breast and prostate cancer. Exposing the colon to less iron seems to decrease the risk of colon cancer. And phytic acid might reduce the side effects of chemotherapy.
One study showed that subjects consuming a Mediterranean-style diet that included 1000-2000 mg of phytic acid per day did not suffer from reduced mineral bioavailability.
At the same time, certain people might have to be more wary.
In particular, iron intake and absorption can be critical for infants nearing six months of age. So when plants are added to infants’ diets, it may be important to adopt strategies to reduce phytic acid and enhance iron absorption.
This is big stuff since myo-inositol phosphates with fewer than five phosphate groups don’t inhibit zinc absorption (IP1 to IP4). And those with fewer than three phosphate groups don’t inhibit iron absorption (IP1 to IP3).
Also, some of the acids produced during fermentation might actually boost absorption of certain minerals.

Non-ruminant animals (e.g., pigs, chickens, dogs, cats) don’t have phytase producing flora, so phytic acid passes through them undigested and makes its way into the soil.
Feeding livestock too much grain can inhibit mineral absorption and increase phosphorus excretion, leading to pollution. Ever heard of the Dead Zone in the Gulf of Mexico?
To argue that some plant foods are “unhealthy” because of their phytic acid content seems mistaken, especially when phytic acid’s potential negative effects on mineral assimilation may be offset by its health benefits.
So we should aim to reduce phytic acid rather than eliminate it.

They’re probably better than 90% of the seminars we’ve ever attended on the subjects of exercise and nutrition (and probably better than a few we’ve given ourselves, too).
The best part? They’re totally free. To check out the free courses, just click one of the links below.
It’s often considered an anti-nutrient because it binds minerals in the digestive tract, making them less available to our bodies.
Yet these same anti-nutrient properties can also help in the prevention of chronic disease.
What is phytic acid?
Seeds — such as nuts, edible seeds, beans/legumes, and grains — store phosphorus as phytic acid. When phytic acid is bound to a mineral in the seed, it’s known as phytate.The tables below compare various seed types according to their phytic acid/phytate content.
Whole grains

Source:
Schlemmer U, et al. Phytate in foods and significance for humans: Food
sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and
analysis. Mol Nutr Food res 2009;53:S330-S375.
Legumes

Source:
Schlemmer U, et al. Phytate in foods and significance for humans: Food
sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and
analysis. Mol Nutr Food res 2009;53:S330-S375.
Nuts

Source:
Schlemmer U, et al. Phytate in foods and significance for humans: Food
sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and
analysis. Mol Nutr Food res 2009;53:S330-S375.
Oil seeds

Source:
Schlemmer U, et al. Phytate in foods and significance for humans: Food
sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and
analysis. Mol Nutr Food res 2009;53:S330-S375
Roots, tubers, and other vegetables may also contain phytic acid, but usually in lower amounts.
The most concentrated sources tend to be whole grains and beans. Phytic acid is isolated in the aleurone layer in most grains, making it more concentrated in the bran. In legumes, it’s found in the cotyledon layer (where the protein is).
Phytate = phytic acid bound to a mineral
Phytates perform an essential role in plants, as they are an energy source for the sprouting seed. When a seed sprouts, phytase enzymes break down the stored phytates. When we eat the plant, phytates are hydrolyzed during digestion to myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexkisphosphate (IP6) and lower inositol polyphosphates including IP1 through IP5 (these are phytate degradation products).
Who’s eating phytic acid?
Everyone who eats plants consumes some phytic acid. It’s all a question of degree.As you can imagine, intake tends to be much higher among those who follow non-Westernized diets. In developing countries, plants are staple foods, which means people eat more of them, and therefore get more phytic acid.
In developed countries, plant-based or vegetarian eaters tend to consume more phytic acid than omnivores. Further, males usually consume more phytic acid than females, simply because they eat more food.
Phytate digestion
Most phytate (37-66%) is degraded in the stomach and small intestines.Ordinarily, our bodies regulate phytate levels pretty well, adjusting uptake in the gut and excretion until body levels come into balance.
Vitamin D status in the body seems to influence how much phytate is actually retained. The more vitamin D, the more phytate retained; the less vitamin D, the less phytate retained.
Potential problems with phytic acid
Phytic acid can bind minerals in the gut before they are absorbed and influence digestive enzymes. Phytates also reduce the digestibility of starches, proteins, and fats.Here’s an example.
Vegan eaters often consume more iron than omnivores. Yet, they also consume more anti-nutrients, including phytates, and these reduce the amount of iron available to their bodies. Consuming 5-10 mg of phytic acid can reduce iron absorption by 50%.
This is why vegetarian eaters should eat more iron than omnivores (33 mg for veg eaters vs. 18 mg for omnivores).
Daily iron loss for men & women
- Adult men lose ~1 mg of iron per day
- Adult menstruating women lose ~1.4 mg/day
- Postmenopausal women lose ~0.8 mg/day
- Lactating women lose ~1.1 mg/day
This can be a good or bad thing, depending on the condition. It’s a bad thing if you’re having trouble building up iron stores in the body and have developed iron-deficiency anemia.
When is it a good thing? Keep reading – you’ll find potential benefits of phytic acid below.
Potential benefits of phytic acid
Despite its potential drawbacks, phytic acid is similar in some ways to a vitamin, and metabolites of phytic acid may have secondary messenger roles in cells.Some experts even suggest that it’s the phytic acid in whole grains and beans that lends them their apparent protective properties against cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
(Remember, the grains with little to no phytic acid are the refined ones.)
The supplement industry has caught on to this. Have you even seen a bottle of inositol hexaphosphate, or IP6? That’s simply a supplemental source of phytic acid.
When phytic acid binds minerals in the gut, it prevents the formation of free radicals, thus making it an antioxidant. Not only that, but it seems to bind heavy metals (e.g., cadmium, lead) helping to prevent their accumulation in the body
Phytic acid’s preventative properties
Cancer
Foods higher in phytic acid seem to enhance the activity of natural killer cells and inhibit tumor growth.Those who consume more phytic acid are less likely to succumb to breast and prostate cancer. Exposing the colon to less iron seems to decrease the risk of colon cancer. And phytic acid might reduce the side effects of chemotherapy.

Source:
Vucenik I & Shamsuddin AM. Protection against cancer by dietary IP6
and inositol. Nutrition and Cancer 2006;55:109-125.
Cardiovascular disease
Phytic acid helps prevent hardening of the arteries and platelet formation.Kidney stones
With some phytate being excreted in the urine, this may improve kidney health and prevent stones.Insulin resistance
Phytic acid plays a role in pancreatic function and insulin secretion. And it may reduce the glycemic response from meals, meaning you feel full for longer.Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis, or iron overload, is a common genetic disorder that phytic acid’s iron-binding properties can protect against or reduce.In the balance
Is phytic acid worth worrying about? Maybe not, for most of us.One study showed that subjects consuming a Mediterranean-style diet that included 1000-2000 mg of phytic acid per day did not suffer from reduced mineral bioavailability.
At the same time, certain people might have to be more wary.
In particular, iron intake and absorption can be critical for infants nearing six months of age. So when plants are added to infants’ diets, it may be important to adopt strategies to reduce phytic acid and enhance iron absorption.
Overcoming phytic acid as an antinutrient
Luckily, it’s possible to overcome the anti-nutrient effects of phytic acid in our foods while still getting the benefits of a plant-rich diet. Here are a few strategies that my be more or less helpful depending on the specific situation:Heat
Heating foods can destroy small amounts of phytic acid. (Note: heat can also destroy phytase and vitamin C.)Processing
Milling grains and removing the bran decreases phytic acid. Unfortunately, milling also tends to remove many of the minerals! Removing the bran and then enriching a food with minerals might allow for enhanced nutrient absorption in the body.Soaking
Soaking beans and grains can reduce phytic acid (and other antinutrients).Fermenting
Fermentation and bread leavening (using yeast) can help to break down phytic acid due to the activation of native phytase enzymes, reducing the number of phosphate groups.This is big stuff since myo-inositol phosphates with fewer than five phosphate groups don’t inhibit zinc absorption (IP1 to IP4). And those with fewer than three phosphate groups don’t inhibit iron absorption (IP1 to IP3).
Also, some of the acids produced during fermentation might actually boost absorption of certain minerals.
Sprouting
Sprouting and malting enhances native phytase activity in plants and thus decreases phytic acid.Vitamin C
Vitamin C appears strong enough to overcome phytic acid. In one study, adding 50 mg of vitamin C counteracted the phytic acid load of a meal. In another study, 80 mg of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) counteracted 25 mg of phytic acid.Protein powders
During processing of plant-based protein powders, it’s possible to de-phytinize (via addition of microbial phytase). Also, protein isolates and concentrates can be treated with dialysis or ultrafiltration to remove phytic acid.Seed breeding
Scientists are working on seed breeds containing less phytic acid. There are modern seed hybrids of grain and legume plants that contain less phytic acid.Animal protein
Animal protein may enhance absorption of zinc, iron, and copper. Adding small amounts of animal protein might increase the absorption of these minerals in the body. (Well, except for dairy/casein, as it also seems to hinder iron and zinc absorption.)Gut health
A low pH in the gut enhances iron absorption. Balancing the level of beneficial bacteria in the GI tract might help with this. See All About Probiotics.
Sprouting enhances native phytase activity in plants and thus decreases phytic acid.
Bonus: Can other animals digest phytic acid?
Ruminant animals (e.g., cattle, sheep, goats, buffalo) possess phytase producing flora for digesting phytic acid.Non-ruminant animals (e.g., pigs, chickens, dogs, cats) don’t have phytase producing flora, so phytic acid passes through them undigested and makes its way into the soil.
Feeding livestock too much grain can inhibit mineral absorption and increase phosphorus excretion, leading to pollution. Ever heard of the Dead Zone in the Gulf of Mexico?
Summary and recommendations
In healthy people eating balanced diets, phytic acid’s effects on iron, zinc, and manganese status is minimal and it doesn’t seem to cause nutrient deficiencies.To argue that some plant foods are “unhealthy” because of their phytic acid content seems mistaken, especially when phytic acid’s potential negative effects on mineral assimilation may be offset by its health benefits.
So we should aim to reduce phytic acid rather than eliminate it.
To reduce the anti-nutrient effects of phytic acid in foods, try the following:
- Soak, sprout, ferment, and cook plant foods.
- Consume vitamin C-rich foods with meals that contain phytic acid. Dense source of vitamin C include guava, bell pepper, kiwi, oranges, grapefruit, strawberries, Brussels sprouts, cantaloupe, papaya, broccoli, sweet potato, pineapple, cauliflower, kale, lemon juice, and parsley.
- Use vinegar in salad dressings and cooking to enhance mineral absorption and offset phytic acid.
- Supplement with phytase enzymes if necessary.
- Eat mineral fortified foods if necessary
- Supplement minerals if there is still a shortfall in your diet.
- If you’re eating a plant-based diet and have confirmed nutrient deficiencies, and you’ve tried all the above strategies with no success, adding small amounts of animal foods on occasion might boost stores of necessary minerals in your body.

Consume vitamin C rich foods with meals that contain phytic acid to offset the effects.
References
Click here to view the information sources referenced in this article.Learn more
To learn more about making important improvements to your own nutrition and exercise program – or, if you’re a fitness professional, to help your clients do the same – check out the following 5-day video courses.They’re probably better than 90% of the seminars we’ve ever attended on the subjects of exercise and nutrition (and probably better than a few we’ve given ourselves, too).
The best part? They’re totally free. To check out the free courses, just click one of the links below.

Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar